You’re entitled to a good night’s sleep. Getting your “beauty sleep” isn’t vain if the alternative is puffy eyes, brain fog, and a lack of motivation. In order to relieve yourself of that under-eye baggage, you may need some assistance. Introducing glycine: an amino acid and neurotransmitter that could help you achieve a fairytale-like ending to your day.
Once upon a time—in 1820 to be precise—European chemist Henri Braconnot discovered glycine through the acid hydrolysis of gelatin.
Glycine, also known as glycocoll, is a crystalline solid as sweet as glucose, thus both names share the Greek word meaning “sweet”: glykys.
Glycine as an Amino Acid
Colorless and odorless, glycine (or aminoacetic acid) is the simplest amino acid found in nature because of its single hydrogen side chain. But its functions are anything but simple: glycine is an essential component of protein synthesis, proper enzyme function, and lipid digestion and absorption.
Glycine Glue: Collagen
Glycine is the primary amino acid in the most abundant protein in our bodies: collagen. You’ve probably heard of collagen; it’s referred to as the magical plumping agent to keep skin looking firm and healthy.
Collagen supports your bones, skin, hair, nails, and more, boosting recovery for sore joints and promoting a healthy gut.
Named after the Greek “kólla” meaning “glue,” collagen’s main function is to hold everything together.
Every third amino acid in collagen must be represented by a strong glycine molecule. If not, the tissue will be unstable. Imagine substituting the leg of a wooden chair with a piece of rolled up paper; the chair will probably collapse. Or maybe it’ll hold until you can trick your friend into trying it out. Either way, mutations resulting in a substitution of the strong glycine molecule can cause connective tissue disorders collectively referred to as brittle bone disease.
In addition to strength, glycine provides flexibility at enzymes’ active sites, allowing them to alter their conformation in order to bind with substrates.
Essential Compounds
Glycine’s connections are particularly important for synthesizing essential compounds. Kind of like a recipe book. Combine glycine with arginine and a dash of methionine and you get the delicious creatine.
Most of your body’s creatine is stored in the muscles as phosphocreatine. Phosphocreatine assists with the production of the body’s stored energy, also known as ATP.
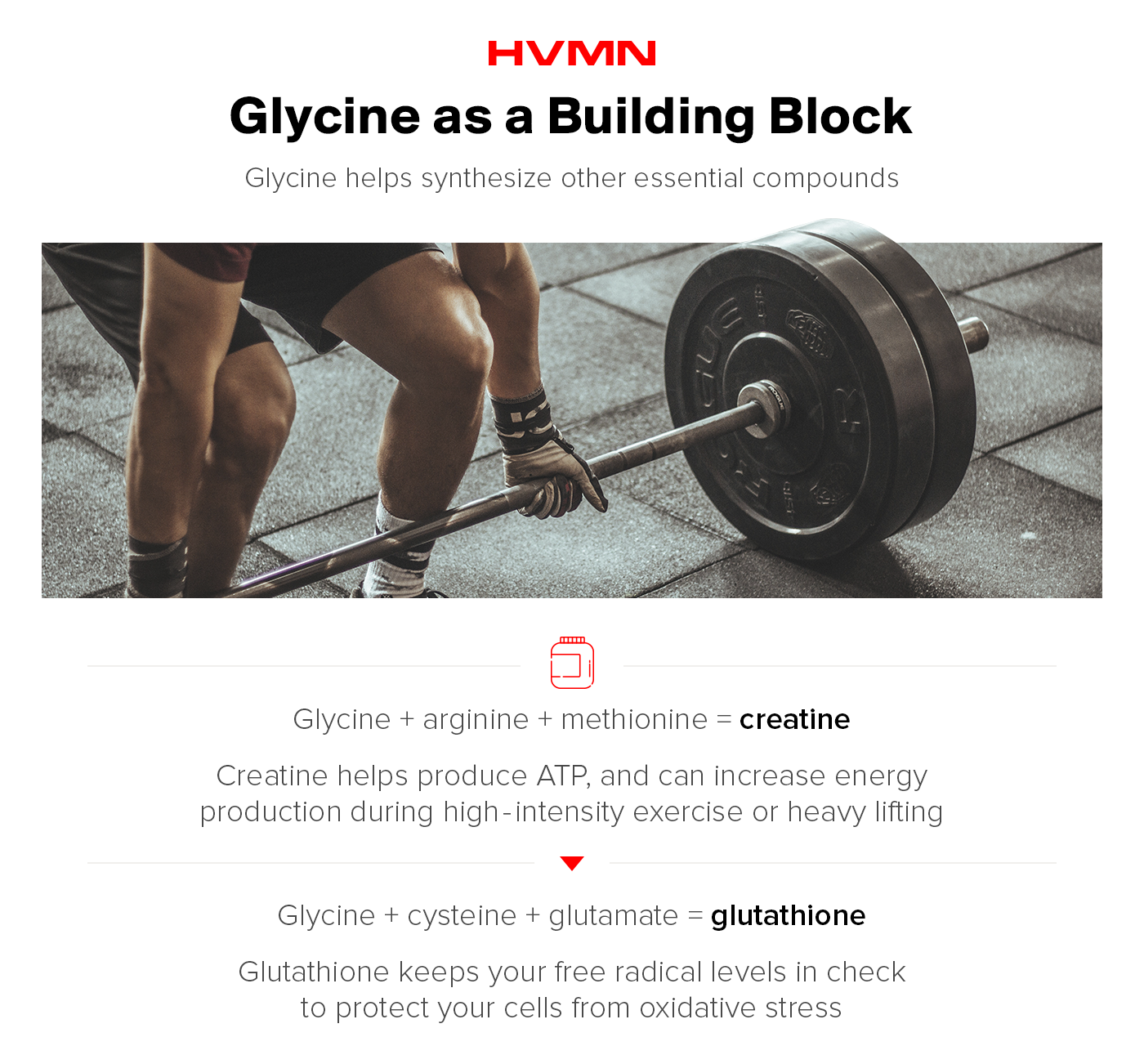
Glycine is one of the main ingredients in glutathione as well. Pair the amino acid with two others, cysteine and glutamate, and you get the non-protein tripeptide known for defending against oxidative stress.
Glycine as a Neurotransmitter
Glycine modulates both inhibitory neurotransmitters and excitatory neurotransmitters in the brain and the spinal cord, regulating reflex coordination, the processing of sensory information, and modulating the pain sensation.
The inhibitory functions of glycine are owed to the glycine-specific receptors in regions of the central nervous system,
Glycine Deficiency
Humans synthesize about 2.5g of glycine every day via serine hydroxymethyltransefrase. Despite being a great vocal warm up, this process doesn’t satisfy our daily 15g metabolic requirement for glycine.
Glycine is a conditionally-essential amino acid; we can survive on the small amount we create, but ideally, we’ll make up the deficit through our dietary choices or supplements. To be considered a non-essential amino acid, our ability to synthesize it would not be related to our dietary intake.
But why would we have such an imbalance between our glycine synthesis and our actual requirements? It may not be very efficient, but you can thank an evolutionary hiccup for this one.
When collagen first appeared as the most abundant protein in small animals, it was only required in amounts relative to size. Smaller animals, smaller needs.
As larger animals evolved, however, they inherited a regulatory system poorly suited to their higher collagen needs. Larger animals, larger needs, and an inability to synthesize enough glycine to satisfy them.
Let’s talk about those needs. Even though glycine is classified as only conditionally-essential, your joints might disagree. According to a meta-analyses of research studies identifying the relationship between collagen and bone health, the glycine-rich glue may increase bone mineral density and have a protective effect on cartilage around the joints.
Humans aren’t alone with their stunted synthesis of this (non)essential compound. Rhinos, elephants, fellow primates,
According to this theory, micronutrient deficiencies could trigger responses that accelerate cancer and neural decay in exchange for maintaining immediate metabolic processes, like production of ATP.
Dietary Sources of Glycine
Collagenous proteins are the primary dietary source of glycine: bone broths, chicken and pork skins, egg whites, milk, and the aforementioned gelatin.
Studies have found that the amino acid composition of the diet is more closely related to glycine production than protein intake. For example, a controlled dietary study of healthy participants found that reducing total protein intake didn’t have an effect on glycine synthesis. However, reducing the amounts of protein exclusively from the essential amino acids (such as histidine and lysine) led to significant reductions in glycine synthesis—a whopping 66%.
Glycine and Cardiovascular Health
Not in love with glycine yet? This amino acid may already have your heart. Or at least the possibility of protecting it.
Heart Disease
Mounting evidence suggests that one of the benefits of glycine is assisting with your battle against heart disease. It has been studied to have numerous inverse associations with coronary risk factors relating to hypertension
Glycine may break down excess compounds associated with low-density lipoprotein formation.
Low-density lipoproteins (LDLs) are the ones that float through your bloodstream and grab onto your arteries for dear life.
Over time, these LDLs accumulate, leaving your arteries clogged and struggling to function normally. Glycine availability may be able to modulate these LDLs to help protect against coronary artery disease.
In a follow-up study of subjects with chest pains, higher glycine levels were associated with a lower risk of both heart disease and heart attacks. While this study does not suggest causality, it does motivate promising research into the mechanism by which glycine may positively affect heart health.
Blood Pressure
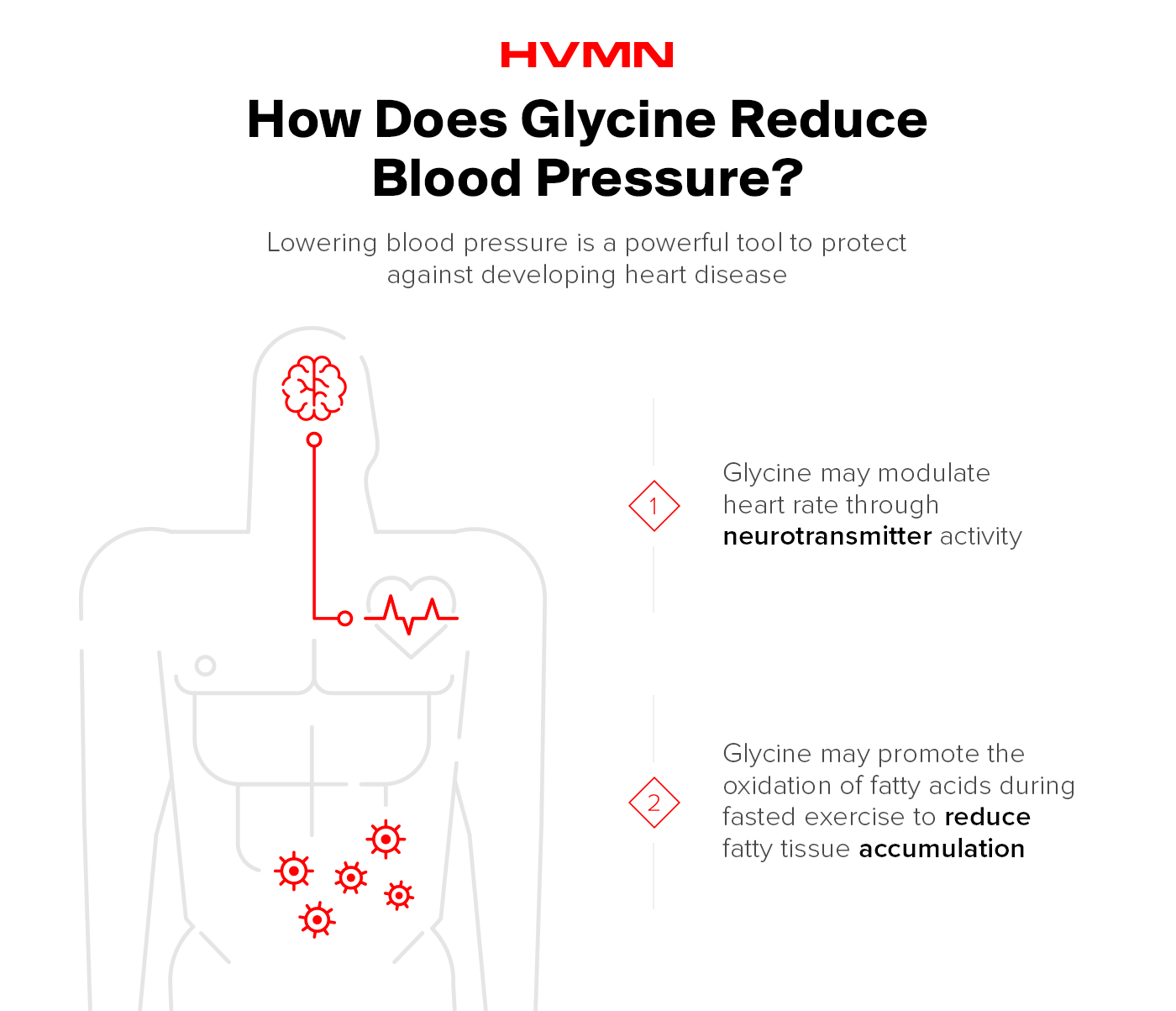
If the potential for protection against heart disease doesn’t get your blood pumping, glycine won’t either. Or at least not in excess—glycine has been investigated for its ability to reduce blood pressure.
But the real pressure is figuring out how glycine is able to do this. It may be through glycine’s neurotransmitter activity, suggesting a reduction of heart rate when the sympathetic nervous system is activated.
Either way, lowering blood pressure is another powerful tool to protect against developing heart disease.
Blood Glucose
Glycine has other business in your blood with its modulation of blood glucose levels. Despite being a sweetener, glycine has been researched for its ability to reduce blood sugar levels.
Post-meal blood sugar levels (also known as postprandial) may experience a reduction because of greater insulin secretion. Glycine has been observed for its ability to increase the release of a peptide that potentiates glucose-mediated insulin secretion when taken with meals.
Glycine: The Sleeping Beauty of Amino Acids
Fixing your sleeping habits shouldn’t be just a fairytale. A good dose of glycine may transform hours of tossing and turning into a restful night’s sleep.
Falling Asleep
Glycine can have a cooling effect on your brain and body. Literally cooling—glycine ingestion has been associated with a decrease in your body’s core temperature, which is a natural accompaniment on its voyage to dreamland.
As body temperature declines, so does your heat production, followed by an increase in your heat loss. All three of these thermoregulation techniques are your body’s way of promoting sleep onset and slow brain wave activity. Conversely, your body’s core temperature begins to increase a few hours prior to waking.
Glycine’s potential to assist with this thermoregulation may explain its link to a quickened ability to fall asleep.
In a study of subjects experiencing problems with falling asleep and dissatisfaction with sleep quality, ingesting a mere 3mg of glycine prior to bedtime was correlated with faster rates of sleep onset.
Your body is a skillful sleep architect—it plans and builds the ideal night of rest to rejuvenate you for the morning. The plan involves cycles of rapid eye movement (REM) sleep and (NREM) sleep correlated with different brain wave patterns and physiology, culminating in your unique slumber skyline.
There are four stages of NREM sleep leading to REM sleep. REM sleep is the deepest stage of sleep you can thank for dreams. There’s no body movement during REM sleep. That’s because your body is protecting itself from physically reacting to your dreams.
Unlike a real building, our unique cityscape snoozing is rather fragile. Disruptions in sleep architecture or irregular cycling is associated with sleep disorders.
Waking Up
In a study on levels of glycine and sleep efficacy, researchers observed that glycine plays a significant role in alleviating symptoms of fatigue in people with poor sleep.
A 2012 study echoed the findings, adding that glycine may be able to improve psychomotor vigilance the morning after ingestion.
Fatigue met its match in glycine—participants reported significant decreases in sleepiness compared to the placebo while their testing performances soared.
This indicates that glycine may have practical implications for those with only occasional sleep restrictions in addition to those with sleep disorders.
Those occasional nights of poor sleep deserve just as much attention as chronic disorders. Certain supplements combine the natural sleep hormone melatonin with stress-reducing

Supplementing with Glycine
If you’re ready to find a happily ever after with glycine, ensure you seek medical advice from your doctor before adding it as a daily supplement.
Clinical trials have dosed glycine up to 0.8g per kilograms of body weight in a healthy adult. For an adult weighing around 175 pounds, that’d be about 64 grams of glycine. Lower daily doses of 15g - 25g have been used in most studies,
While no major adverse effects of glycine supplementation have been reported, mild side effects have been reported. Mild side effects include abdominal pain and soft stools, with abdominal pain generally reported when taking glycine on an empty stomach. Ingesting glycine during meals is not associated with causing daytime sleepiness.
Give it a Rest
Whether you’re looking for a better night’s sleep to fuel long workdays or want to ensure you’re hitting your evolutionarily-stunted metabolic needs, glycine may be able to help you achieve your goals.
Along the way, this powerhouse amino acid may be able to offer protection against the atherosclerotic process to boost heart health. Another heart helper? Glycine’s promising modulations of blood glucose levels in normal adults and those with blood glucose sensitivity problems.
Even if you’re not a fan of love stories, rest assured that you and glycine could live happily ever after.
Editors Choice

How to Get Into Ketosis Fast
The low-carb, high-fat keto diet has been shown to improve body composition and increase endurance performance. But getting into ketosis is difficu...

Ketones in Urine: All You Need to Know
Monitoring ketone levels in urine is important for both diabetics and those waiting to maintain ketosis. Here's what to look for, how to test and t...

VO2 Max: Training to Use Oxygen Efficiently
VO2 max might be the truest representation of endurance fitness there is. While elite runners and cyclists train their bodies to use a high volume ...

Do Calories Matter on a Keto Diet?
Are all calories created equal? Not on the keto diet. Weight loss has emerged as a primary incentive for going keto. That's not driven by the amoun...

Keto Diet Fundamentals
A ketogenic diet, or “keto diet,” refers to an extremely low-carbohydrate, high-fat pattern of eating. This article dives into the history of the k...

Beta-hydroxybutyrate or BHB –All You Need to Know
BHB stands for beta-hydroxybutyrate, one of the three main ketone bodies. It's a clean-burning energy source for both the body and the brain. What'...

Ketone Salts: Ketosis with a Cost
Ketone salts, also known as BHB salts, provide the body with a way to enter ketosis. But the results are mixed. There are a few options for someone...

How to Run Faster: Mental and Physical Techniques
Runners chase speed. For many, it's a lifelong pursuit. The connection between the body and the mind is important for speed, and harnessing both wi...

